The Deutz 914 series represents one of the most recognized air-cooled diesel engine families in industrial and agricultural machinery worldwide. These engines have powered everything from telehandlers and compressors to farm tractors and stationary generators for decades, earning a reputation for rugged reliability in harsh operating conditions.
If you’ve encountered a 914 in the field or are researching used equipment, you likely have questions about performance, known issues, and whether the rumors about these engines being “banned” have any truth to them. This guide covers the essential details you need to know.
Deutz 914 Series Engine Overview
The Deutz 914 family includes air-cooled diesel engine configurations ranging from compact 3-cylinder units (such as the D 914 L3 or F3L914) up to powerful 6 cylinder models (like the TCD 914 L6 and F6L914). DEUTZ AG, the German manufacturer behind this series, produced these engines primarily from the mid-1990s through the 2010s, building on their legacy of modular, serviceable power units.
These engines were designed for off-highway equipment where reliability matters more than cutting-edge emissions technology. Depending on the specific model and production year, the 914 series covers emissions levels from Tier 2 through Tier 3, with certain TCD 914 models under 56 kW achieving Tier 4i certification for US EPA compliance.
You’ll find 914 engines across a wide range of application areas:
- Telehandlers and material handlers
- Industrial generators and stationary power units
- Farm tractors and agricultural equipment
- Mobile and stationary compressors
- Construction machinery and earthmoving equipment
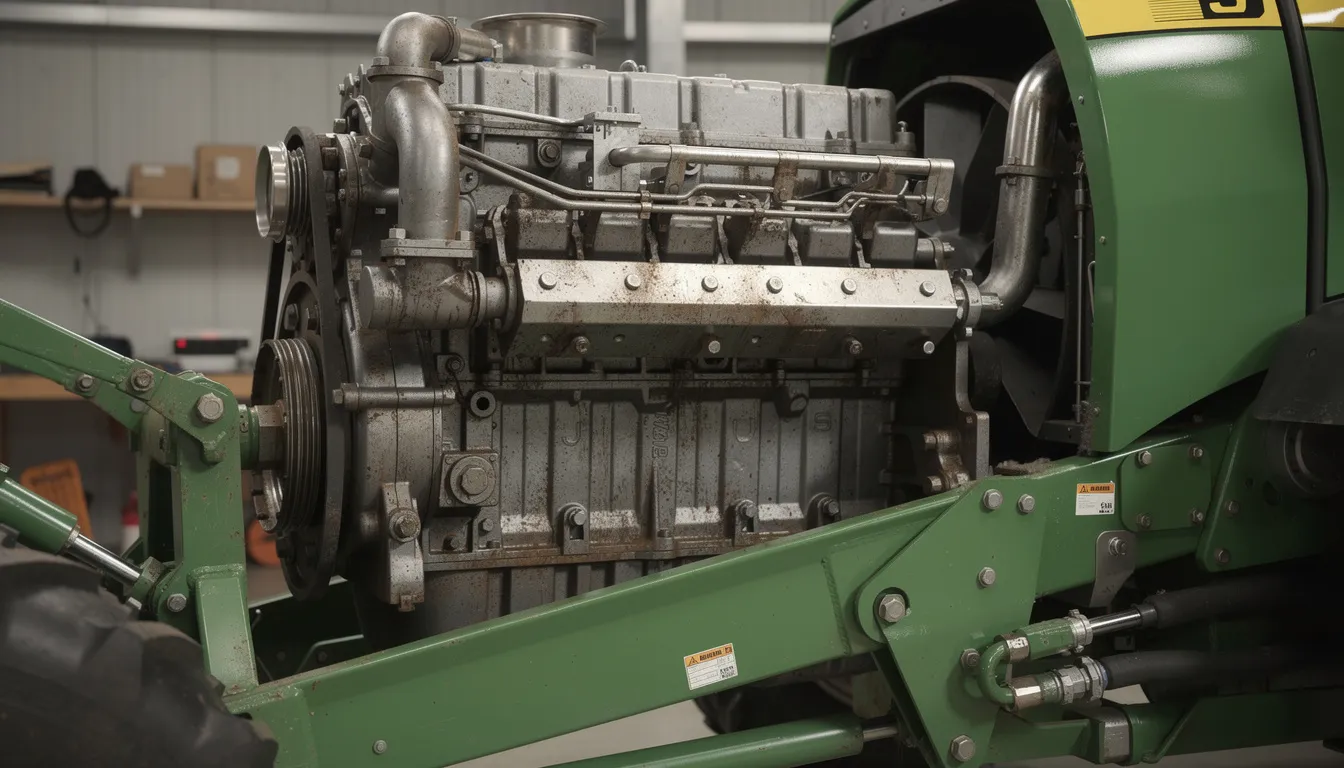
Deutz 914 Engine Vairants and Configurations
The “Deutz 914” designation covers a family of engines rather than a single model. Understanding the naming conventions helps when sourcing parts, reviewing technical data, or evaluating used equipment.
The model codes tell you key details about each engine:
- F indicates air-cooled design
- L refers to inline arrangement of cylinders
- Numbers (3,4,6) specify the number of cylinder
- TCD stands for Turbocharged, Charge-air cooled, Diesel
Main Mechanical Variants
The 914 series uses a modular single-cylinder construction with 1.1 liters of displacement per cylinder. This design allows DEUTZ to offer consistent build quality across the range while scaling power output through the number of cylinders.
|
Model Series |
Cylinders |
Configuration |
Typical Power Range |
Emissions Level |
|
F3L914 / D 914 L3 |
3 |
Inline, air-cooled |
~43-50 kW (58-67 hp) |
Tier 2/3 |
|
F4L914 / BF 4L 914 |
4 |
Inline, air-cooled |
~55-75 kW (74-101 hp) |
Tier 2/3 |
|
F6L914 |
6 |
Inline, air-cooled |
~85-100 kW (114-134 hp) |
Tier 2/3 |
|
TCD 914 L6 |
6 |
Inline, turbocharged |
~100-130 kW (134-174 hp) |
Tier 3/4i |
The Tier 3 and Tier 4i compliant versions appear primarily in the TCD 914 L6 range, particularly in power classes under 56 kW where US EPA Tier 4 interim standards apply.
Technical Specifications of the Deutz 914 Series
Understanding the core technical data helps with parts identification, maintenance planning, and evaluating whether a 914 engine fits your application requirements.
Core Engine Dimensions
- Bore: 102 mm
- Stroke: 132 mm
- Displacement: Approximately 1.1 liters per cylinder
- Compression ratio: Around 21:1
- Nominal speed range: 2000-2300 rpm
The 21:1 compression ratio contributes to strong torque output and efficient combustion while meeting the emissions standards of the production era. This ratio also supports reliable cold starting in demanding conditions.
Power Range Across Models
The available power range spans from roughly 43 kW (approximately 58 hp) in smaller 3-cylinder versions up to around 129-130 kW (about 174 hp) in the TCD 914 L6. This broad range means you can find 914 engines in equipment from compact utility machines to larger construction and agricultural units.
Specific fuel consumption values reach as low as approximately 218 g/kWh in well-tuned configurations. However, actual figures depend heavily on load conditions, engine configuration, and maintenance status. Some genset applications report consumption rates around 204-205 g/kWh at 75-100% load under continuous power operation.
The engines use mechanical direct injection systems, with later configurations incorporating internal exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) for improved emissions control. This highly efficient injection design provides precise fuel metering across the operating RPM range.
Torque, Fuel Efficiency and Operating Characteristics
Users value the 914 series for its torque curve and fuel economy in continuous-duty applications. The engines deliver strong pulling power at relatively low speeds, which suits industrial and agricultural duty cycles.
Torque output by configuration:
- 3-cylinder models: 200+ Nm peak torque
- 4-cylinder models: 300-400 Nm typical range
- TCD 914 L6: Up to approximately 650 Nm
Maximum torque arrives at relatively low engine speeds, typically between 1400-1600 rpm depending on the model. This characteristic proves valuable for equipment that operates under variable loads.
The low specific fuel consumption (around 0.358 lb/hp-hr in many configurations) helps reduce operating costs for fleet owners and rental companies running equipment continuously. For a construction compressor running 10 hours daily, this efficiency translates directly to lower fuel bills over the service life.
Recommended idle speeds typically fall between 650-700 rpm depending on the model. A stable low idle benefits equipment such as generators and compressors where consistent power delivery matters. Farm tractor operators often appreciate the smooth power delivery across the RPM range when working varied terrain.
Design Features: Durability, Cooling and Noise
The Deutz 914 was engineered as an air-cooled, robust platform aimed at harsh environments and long service intervals. This design philosophy shows in the construction details and component choices.
Modular Single-Cylinder Construction
The modular approach means each cylinder functions as a self-contained unit. This simplifies service and overhauls compared with some water-cooled competitors. A technician can address problems with individual cylinders without extensive disassembly of surrounding components.
Over 3 million DEUTZ engines from this family and related series have proven themselves in worldwide operation, demonstrating the effectiveness of this construction approach.
Air-Cooling System
The air-cooling system features large finned cylinders and a high-capacity fan that moves air across the engine surfaces. This design offers significant advantages:
- No radiator to maintain or repair
- Eliminates coolant freeze risk in cold climates
- Removes boiling concerns in hot environments
- Reduces potential failure points
- Simplifies operation in dusty or remote locations
For equipment working in desert conditions, remote mining sites, or dusty agricultural environments, air cooling reduces maintenance complexity substantially.
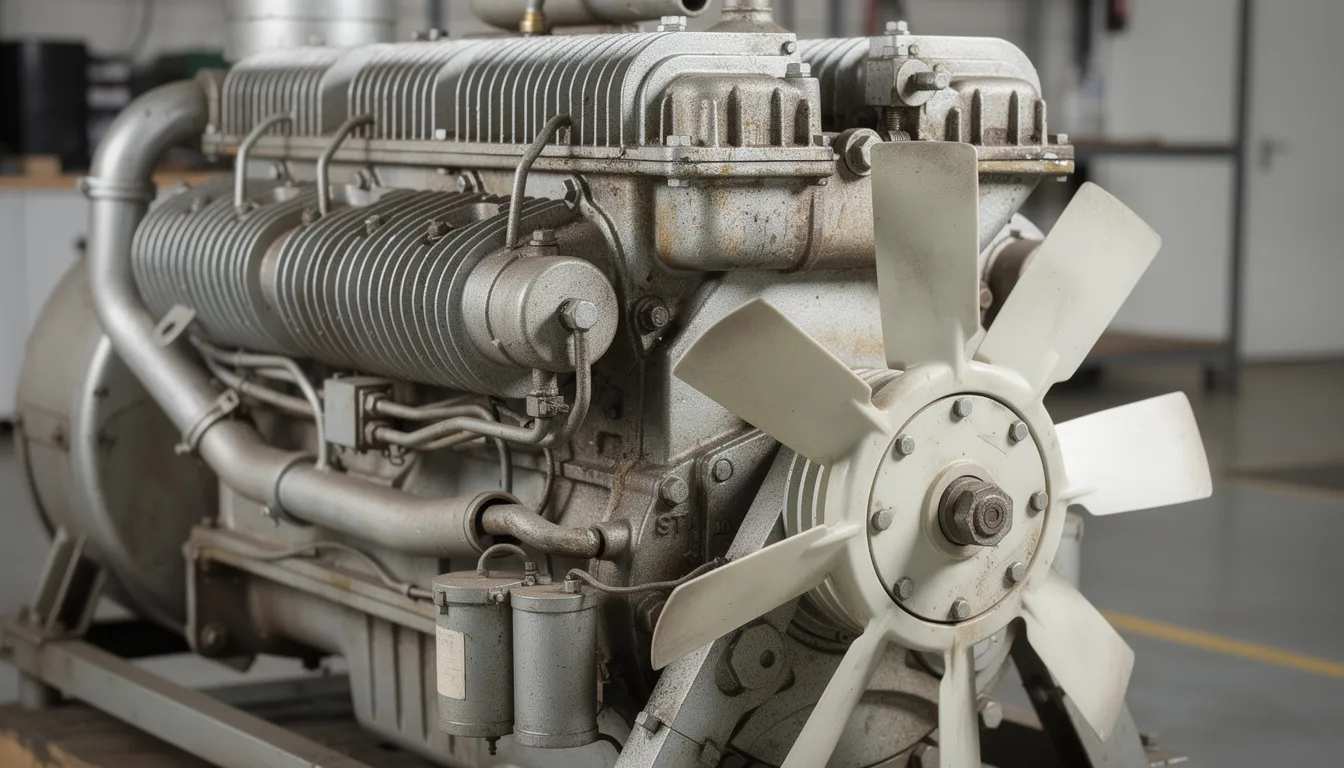
Noise and Weight Considerations
Models like the TCD 914 L6 incorporate acoustically optimized components that reduce mechanical noise and vibration. This improves operator comfort on modern machines and helps meet workplace noise regulations in some jurisdictions, contributing to low noise emissions overall.
Typical dry weight ranges from roughly 277 kg for smaller 3-cylinder versions to about 510 kg for the full 6 cylinder TCD 914 L6. This weight profile supports compact machinery layouts while maintaining the structural integrity needed for high durability in demanding applications.
The heavy-duty crankcase, proven injection equipment, and robust internals contribute to a design life suitable for thousands of operating hours when maintained correctly. Many operators report engine life exceeding 10,000 hours with proper service attention.
Advanced Technology and Emissions Control
Later 914 variants integrated simple but effective technologies to meet tightening emission regulations without sacrificing the simplicity that made the series popular.
The switched internal EGR system on some 914 engines works by recirculating a portion of exhaust gas back into the combustion chamber. This lowers combustion temperature and reduces nitrogen oxide (NOx) formation—a key concern for emissions compliance.
Many 914 engines retain a fully mechanical injection system. This approach balances reliability with emissions performance for non-road applications where electronic complexity might create maintenance challenges. The absence of complex digital controls appeals to operators in remote locations or developing markets.
Models achieving certification typically meet standards like ISO 14396 for power rating and US EPA Tier 3 or Tier 4 interim in specific power categories. Some configurations also accommodate higher-sulfur diesel fuel, which remains relevant for export applications and remote operations where premium fuel isn’t available.
TCD 914 L6: Flagship Model Highlight
The TCD 914 L6 represents the flagship of the 914 family—a 6 cylinder turbocharged, charge-air-cooled diesel engine maintaining the proven 1.1 liter per cylinder displacement.
Hardware and Performance
The engine features an inline-6 layout with turbocharging for improved power density. Charge-air cooling brings intake air temperature down after compression, resulting in denser air charge and improved combustion efficiency. The mechanical injection system delivers fuel with precision for optimum engine performance.
This configuration produces up to approximately 130 kW (about 174 hp) per ISO 14396 standards, placing it in the upper power range of the 914 family. The combination of turbocharging and charge-air cooling supports Tier 3 and Tier 4i emissions levels in configurations under 56 kW.
Common Applications
The TCD 914 L6 appears frequently in:
- Larger construction machinery requiring sustained power
- Mobile compressors for industrial and oil field use
- Agricultural machines with high power demands
- Material handling equipment
The engine’s reputation includes smooth running characteristics and relatively quiet operation thanks to acoustically optimized components—a benefit for operators spending long hours around the equipment.
Maintenance Focus Areas
Typical maintenance tasks for the TCD 914 L6 include:
- Oil and filter changes at recommended intervals
- Air filter inspection and replacement
- Valve clearance checks and adjustment
- Fan belt inspection and tensioning
- Turbocharger inspection for shaft play and seal condition
- Fuel system component checks
Keeping the cooling fins clean remains essential for air-cooled engines. Compressed air or soft brushes help remove debris that can reduce cooling efficiency and lead to overheating.
"Why Deutz 914 Was Banned" - Clarifying Myths vs. Regulations
There is no universal global “ban” on the Deutz 914 engine. What actually occurred is a gradual regulatory phase-out that affects new engine sales in certain markets—not a prohibition on existing equipment.
What Actually Happened
Stricter emission regulations such as EU Stage V and updated US EPA non-road standards have limited the sale of new Tier 2 and Tier 3 engines in the European Union and North America after specific cutoff dates. This means manufacturers cannot sell new engines of these emissions levels for installation in new equipment in regulated markets.
However, several important points apply:
- Machines already in service with 914 engines are typically allowed to continue operating
- Used equipment with 914 engines can still be bought, sold, and operated
- New engine sales must comply with current emission tiers in regulated markets
- Replacement engines for existing equipment often have different rules than engines for new machines
- Many global markets outside the EU and North America have less restrictive requirements.
A Practical Example
Consider a contractor in 2024 who owns a compressor powered by an F4L914 engine. That machine can continue operating legally in most jurisdictions. If the engine fails, parts remain available for rebuild. However, the same contractor cannot purchase a brand-new Tier 2 F4L914 engine for installation in a new compressor destined for EU or US markets.
When maintained according to DEUTZ specifications, the 914 has a long record of safe operation in compressors, generators, mobile equipment, and stationary applications. The “banned” narrative often conflates regulatory compliance requirements with safety concerns that don’t reflect standard industrial use.
Parts, Service and Support for Deutz 914 Engines
Despite regulatory changes affecting new engine sales, Deutz 914 engines remain widely supported with both genuine and aftermarket parts. The installed base of these engines ensures continued demand for service components.
Models Commonly Requiring Parts Support
- F3L914 and D 914 L3 three-cylinder units
- F4L914 and BF 4L 914 four-cylinder configurations
- F6L914 six-cylinder naturally aspirated models
- TCD 914 L6 turbocharged units
These engines appear in generators, compressors, tractors, and various construction equipment, maintaining steady parts demand.
Sourcing Quality Components
Genuine or OEM-quality parts matter for maintaining reliability and emissions performance. Key components to source carefully include:
- Pistons, liners, and ring sets
- Gasket sets and seals
- Fuel injection pumps and injectors
- Air, oil, and fuel filter elements
- Cooling fan components and belts
- Governors and speed control components
- Flywheel and flywheel housing parts
The perfect fit of these components ensures continued performance matching original specifications.
Working with Suppliers
An authorized DEUTZ service dealer or specialist can help identify correct parts by engine serial number and build list. Given the number of 914 variants produced over the years, this identification step proves critical for getting the right components.
Typical wear items and service intervals:
|
Component |
Typical Interval |
|
Engine oil and filter |
250-500 hours depending on conditions |
|
Air filter element |
Inspect regularly, replace as needed |
|
Fuel filter |
500-1000 hours or annually |
|
Valve lash check |
1000-2000 hours |
|
Fan belt inspection |
Every service, replace if cracked |
|
Injection nozzle check |
2000-3000 hours |
Many suppliers offer phone support and online quote request options for 914 parts. Have your engine model designation and serial number ready when contacting support to improve the speed and accuracy of quotes. You can visit Fab Heavy Parts to confirm part availability for your specific engine.
Applications, Buying Advice and Conclusion
Deutz 914 engines remain common in used machinery markets, stationary power units, older tractors, and construction equipment. Understanding where these engines excel—and where they don’t—helps with purchase decisions.
Where You'll Find 914 Engines Today
- Used telehandlers and material handling equipment
- Older agricultural tractors and implements
- Stationary and portable generators
- Industrial compressors
- Construction equipment in developing markets
- Backup power installations
Buying Tips for Used 914-Powered Equipment
When evaluating equipment with a 914 engine, check these key areas:
- Hour meter reading – Verify consistency with overall machine condition
- Service records – Look for regular oil changes and major service documentation
- Cold start behavior – Easy starting indicates good compression and injection system
- Oil consumption – Excessive consumption suggests worn rings or guides
- Exhaust smoke – Blue smoke indicates oil burning; black smoke suggests injection problems
- Cooling fan condition – Check belt tension, fan blade condition, and shroud integrity
- External oil leaks – Inspect around cylinder bases, timing cover, and crankcase
When a 914 Makes Sense
The 914 remains a strong choice for:
- Remote location operations where air-cooling simplicity prevents downtime
- Applications where installation costs benefit from compact, lightweight design
- Equipment where mechanical simplicity aids field service
- Developing markets without strict emissions enforcement
- Backup or standby power where occasional use doesn’t justify newer technology
Consider a newer, cleaner engine family when:
- Operating in strict urban emissions zones
- Projects require EU Stage V or US Tier 4 Final compliance
- Electronic integration with equipment management systems is required
- Fuel efficiency is the primary operating cost concern
Final Thoughts
The Deutz 914 series earned its reputation through decades of service in demanding applications worldwide. The experience of millions of operating hours across agriculture, construction, and power generation confirms what operators have long known: these engines deliver high durability and reliable performance when maintained properly.
The “banned engine” narrative misrepresents regulatory realities. While you cannot install a new Tier 2 914 in equipment bound for regulated EU or North American markets, existing machines continue operating legally, parts remain available, and the engines themselves function exactly as designed.
For equipment owners and buyers evaluating 914-powered machines, the fundamentals haven’t changed. Check condition carefully, maintain according to specifications, source quality parts, and these engines can deliver thousands of additional operating hours. The technical data supports continued confidence in properly maintained units.
Ready to identify your specific 914 engine or source the correct components? Contact a knowledgeable DEUTZ specialist or authorized dealer with your engine model and serial number. Having these details ready makes the process of getting parts quotes and service recommendations straightforward and ensures you receive options relevant to your exact configuration. You can also visit Fab Heavy Parts, to confirm part availability and browse a wide selection of parts for Deutz 914 engine.
Shop Replacement Parts Fit for Deutz 914 Engine
FAB Heavy Parts: Your Trusted Engine Parts Supplier
Welcome to Fab Heavy Parts' online catalog, your trusted source for quality auto parts and tools. Explore our extensive selection of replacement parts for Deutz 914 Engine and more. Avoid delays by securing the parts you need from a reliable supplier who keeps inventory moving. Our expert team is here to provide personalized support, ensuring you get the right parts. Reach out today to stay ahead and keep your operations seamless!
Interested in exploring products that are compatible with the Deutz 914 Engine? Check out our Product Highlight for recommendations on the best accessories to enhance your machine's performance.

